New EGRN-GNET Report: 30 Years of Trends in Terrorist and Extremist Games

Violent extremist, terrorist, and targeted hate actors have been actively exploiting video games to propagandise, recruit and fundraise for more than 30 years. This report presents an analysis of that history using a unique dataset, the Extremist and Terrorist Games Database (ETGD), developed by the authors. It contains 155 reviewed entries of standalone games, modifications for […]
Camera, Action, Play: An Exploration of Extremist Activity on Video- and Livestreaming Platforms

Introduction Since the livestreamed attacks in Christchurch, Halle and the US Capitol Building, streaming platforms have become a topic of interest for radicalisation studies and efforts to prevent and counter (violent) extremism (P/CVE). These livestreamed acts of violence are just the tip of a barely explored iceberg of extremist activities on streaming platforms. While existing […]
Gaming the System: The Use of Gaming-Adjacent Communication, Game and Mod Platforms by Extremist Actors

Introduction Since the live-streamed racist and antisemitic attacks in Christchurch, New Zealand, and Halle, Germany, in 2019 and details of the perpetrators’ profiles on gaming platforms became known, a discussion about the use of gaming platforms and content by extremist actors has intensified. However, despite this increased interest, reliable research results about the field are […]
More than Sports: Building Resilience against Extremism in Esports
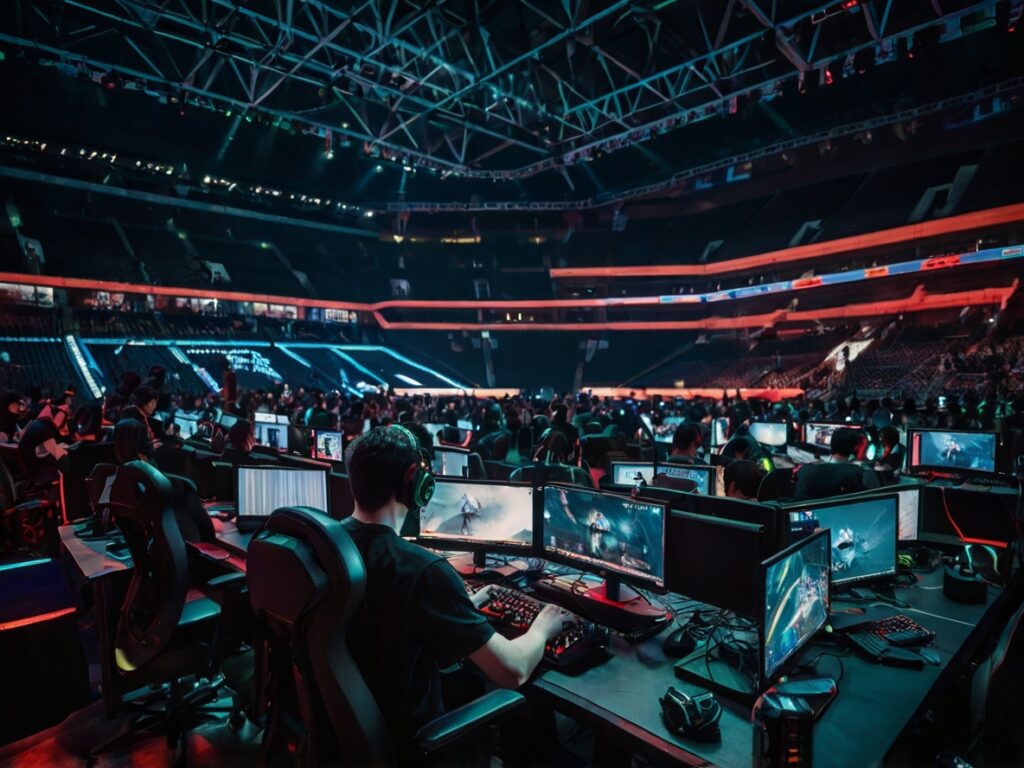

In a world where young people spend most of their time online, gamers are at risk of encountering radicalizing content more often than others. The United States Esports Association has taken up the challenge of addressing these issues through competency-building initiatives aimed at combatting violent extremism. Read on to find out more about the potential risks of esports and the Association’s innovative solutions.
Preventing Extremist Violence Using Existing Content Moderation Tools

Accurate content moderation can save lives by acting as an early warning system about the risks of offline extremist violence and removing the fuel that incites it. With the explosion in automated content moderation approaches, any number of widely accessible automated detection tools can be used on known violent extremist user-generated content to improve a platform’s detection methods through fine-tuning and customization. Multiple AI-based approaches to detection can identify users, conversations, and communities, signaling a high likelihood of extremist violence. With better real-time detection, platforms can be empowered to break up harmful and criminal communities, helping to damage online influence processes that lead to extremist violence.
Grooming for Violence: Similarities Between Radicalisation and Grooming Processes in Gaming Spaces
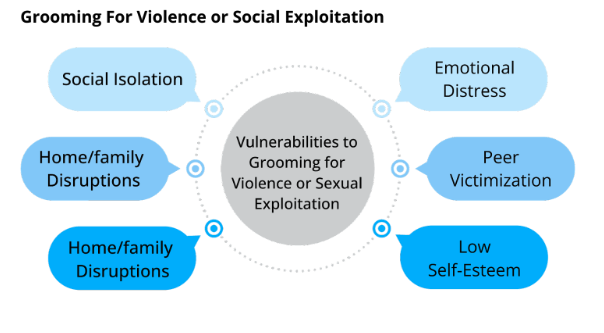
Some scholars have identified similarities between a subset of radicalisation to violent extremism (RVE) processes and grooming for CSE. Though RVE and CSE grooming and processes can happen in a variety of online and offline spaces, greater awareness of these risks in gaming spaces in particular is important due to the ways in which many games facilitate relationship building with limited moderation.
Accelerationism Meets Gamification: A Look at the Convergence in the Framing of Online Narratives

Petra Regeni is a member of the Extremism and Gaming Research Network (EGRN). EGRN brings together world-leading counter-extremism organisations to develop insights and solutions for gaming and radicalisation. This article was originally published in conjunction with our partner, GNET, as an Insight on 31 May 2023. Introduction For many, words like ‘high score’ and ‘accelerate’ mean nothing […]
